Hi, everyone. Hope everything is going well with you.
This time I’d like to talk about the structure of Dynamics 365 Business Central.
SaaS
First let’s look at the structure of SaaS.
The following figure shows the structure of the data in Business Central SaaS.
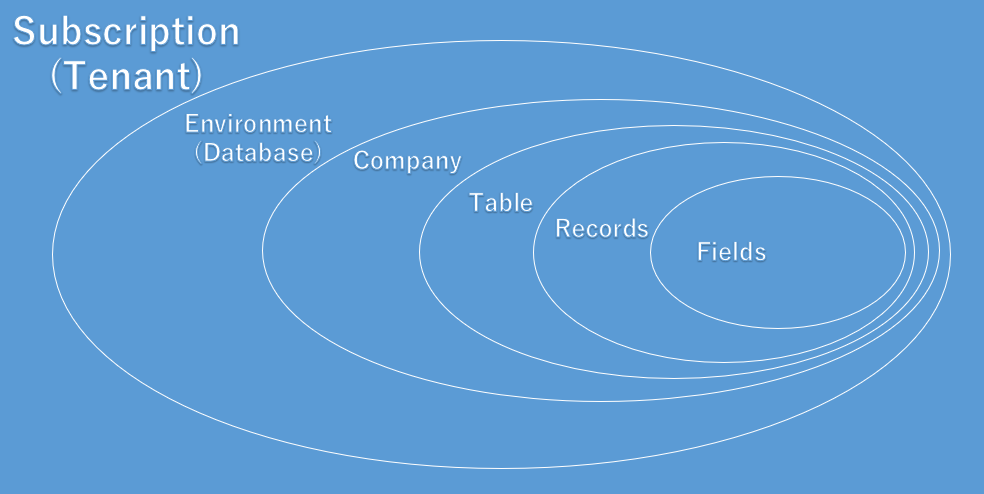
Subscription:Business Central is a Subscription-based software in SaaS, it relates to a monthly or annual licensing model, allowing users to pay a per user fee. Customers typically pay an initial subscription upfront, and are entitled to use the software only during the subscription term, unlike a perpetual license, allowing them to use software indefinitely. The subscription payment includes software licenses, access to support services and new versions of the software as they are released.
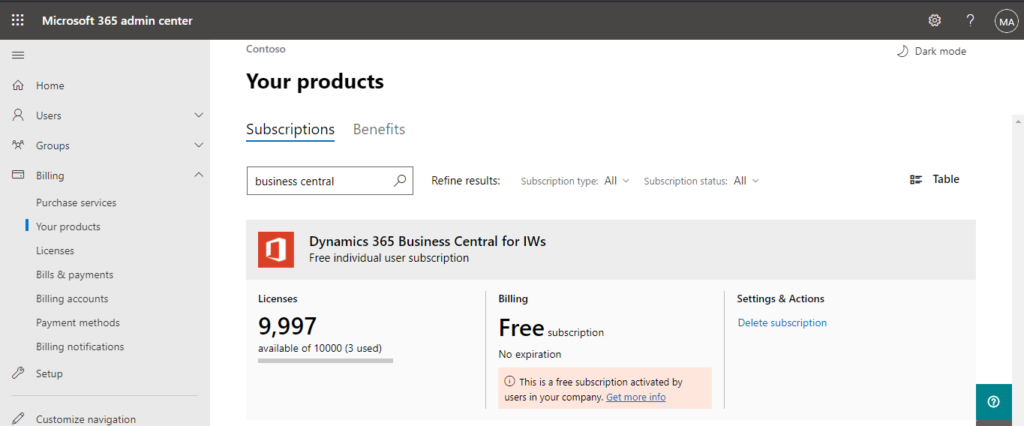
You can manage subscriptions in Microsoft 365 admin center.
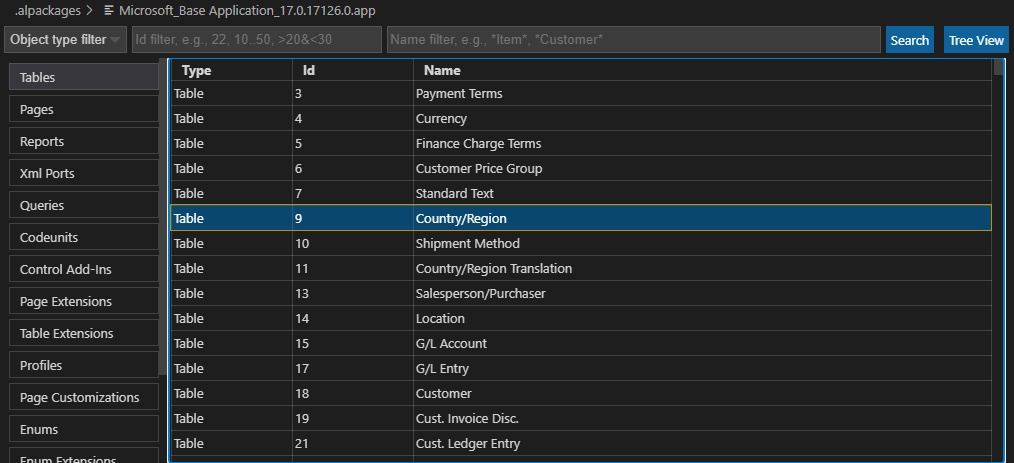
Environment: Each environment is an independent database of Business Central. You can create environments of different types in Dynamics 365 Business Center admin center. (Production and Sandbox Environments)
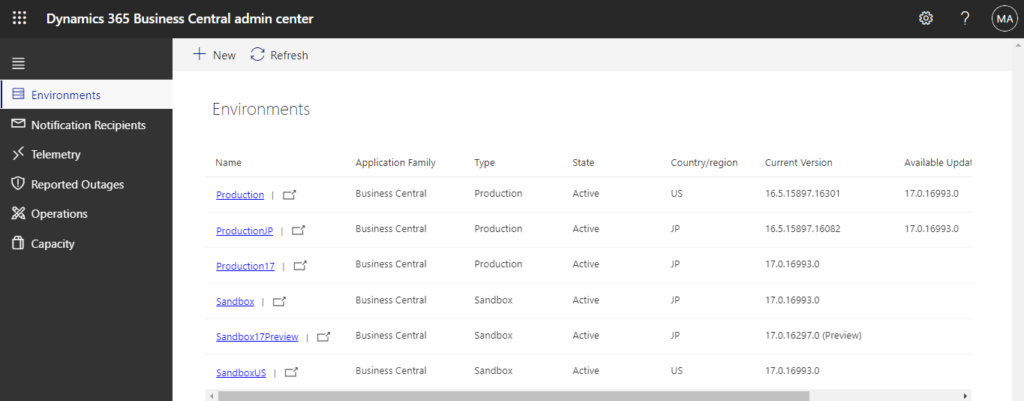
The Premium and Essential subscription types give each Business Central customer one production tenant and three sandbox tenants free of extra charge. If the customer requires more production tenants, they can buy additional tenants through their CSP partner. Each additional production environment comes with three additional sandbox environments and 4 GB additional, tenant-wide database capacity.

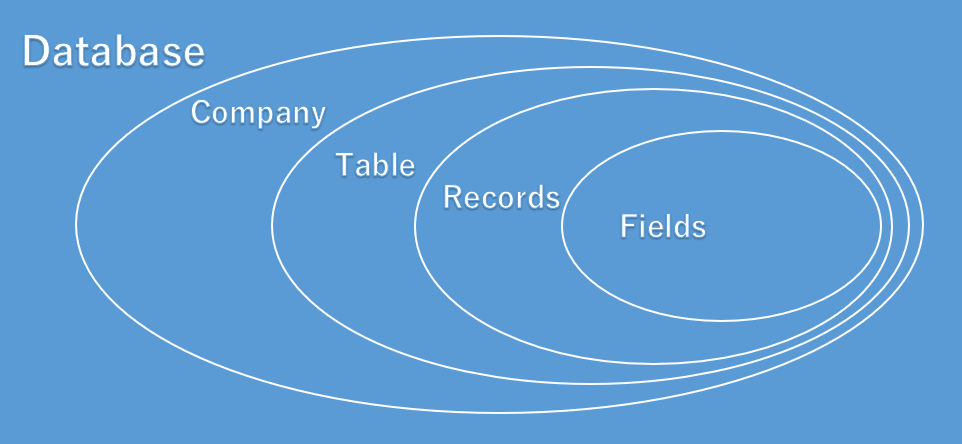
Company: A company is the largest logical structures that is used in a Business Central database. A company may be considered as a sub database. its primary use is to separate and group large sections of data in a database. A company can contain private tables and tables that are shared with other companies.
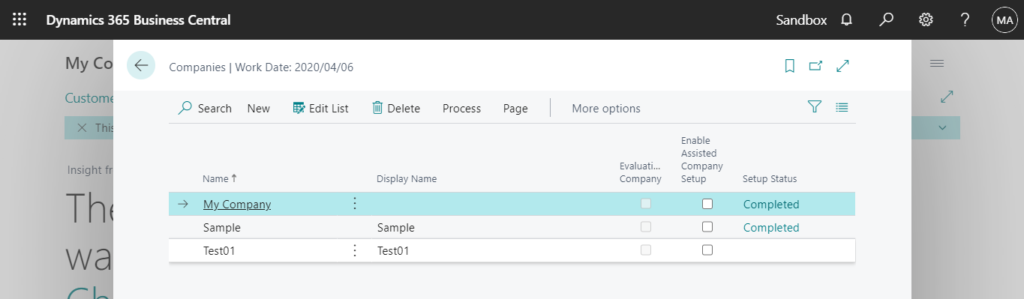
You can use DataPerCompay property in tables to indicates whether the table data applies to all companies in the database or only the current company.
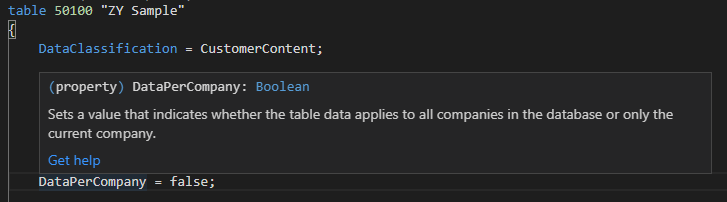
Table:Think of a table as a matrix. Each row describes a record and each column describes a field in the record. Tables are organized in companies.
Record:A record is a logical structure that is assembled from an arbitrary number of fields. Fields are used to store a single entry in a database. The fields in a record store information about entity properties that are represented by record. Records are organized in tables.
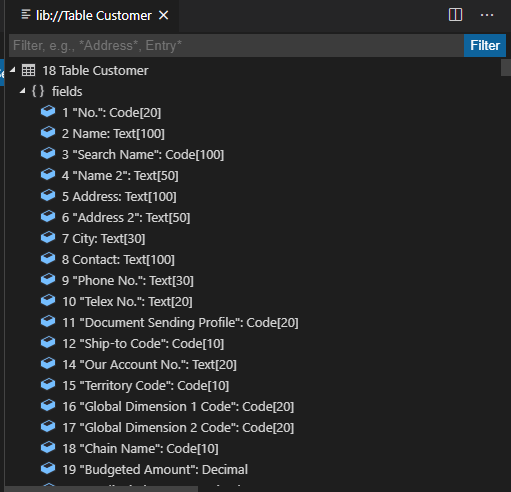
Field: A field is the smallest logical structure that is used in a Business Central environment (Database). A field contains a single piece of information, such as a number or a name. A field can contain only one specific type of information.
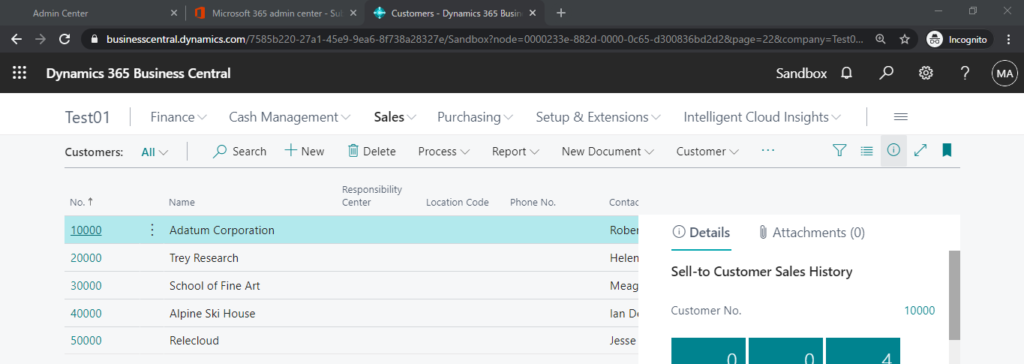
So, when you open a page on SaaS, you will definitely notice the URL.
For example:
“https://businesscentral.dynamics.com/7585b220-27a1-45e9-9ea6-8f738a28327e/Sandbox?node=0000233e-882d-0000-0c65-d300836bd2d2&page=22&company=Test01&dc=0&bookmark=21%3bEgAAAAJ7BTEAMAAwADAAMA%3d%3d”
Tenant ID: 7585b220-27a1-45e9-9ea6-8f738a28327e
Environment Name: Sandbox
Page Number: 22
Company Name: Test01
On-Premises
The structure of Business Central On-Premises is same as Dynamic NAV.
The following figure shows the structure of the data in Business Central On-Premises.
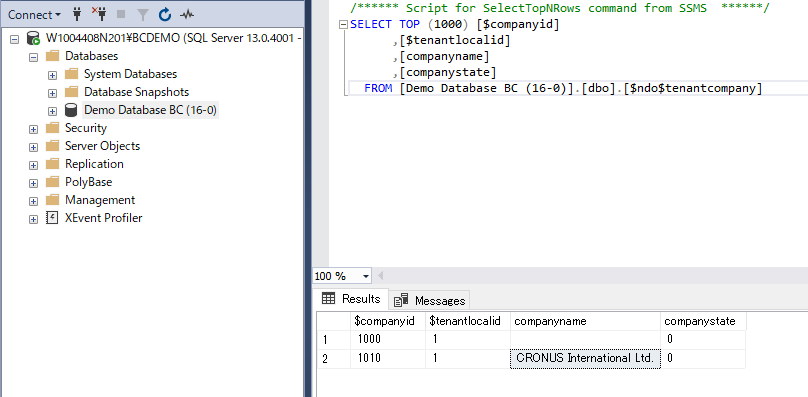
You can access the Business Center database on the database server.
Database and Companies:
Tables and field:
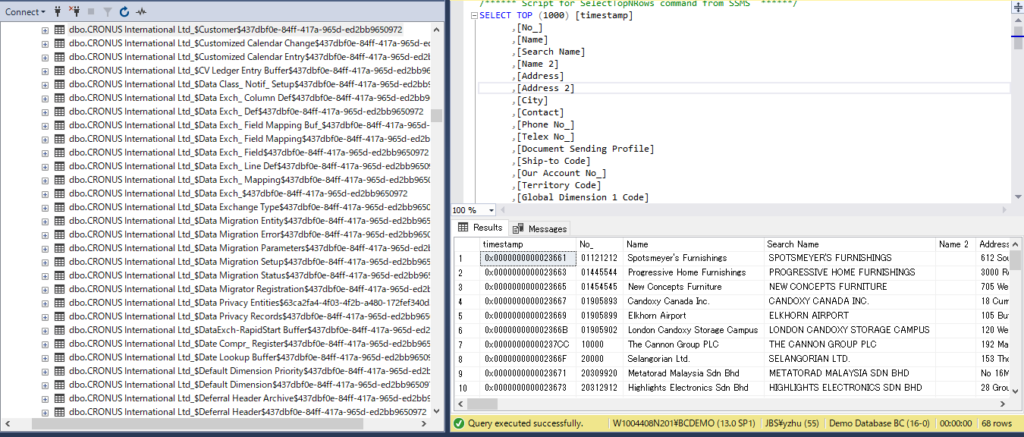
Other information is the same as SaaS, you can refer to the above descriptions of SaaS.
END
Hope this will help.
Thanks.



コメント